Episodes of Short Science Explained
Mark All
Today we’re diving into the incredible story of how our solar system came to be. From a swirling cloud of gas and dust to the formation of planets, let’s take a journey through time—about 4.6 billion years ago!"
Mars, Europa, and Enceladus are promising locations for the search for microbial life within our solar system.The search for intelligent life, through efforts like SETI, is ongoing, but the vastness of the universe makes it a challenging task.E
The Multiverse Theory posits that our universe is one of many parallel universes.The Quantum Multiverse arises from quantum mechanics, suggesting new universes are created with every decision.The Cosmological Multiverse comes from the idea of c
Dark matter accounts for 27% of the universe and helps explain how galaxies hold together.Dark energy, making up 68% of the universe, is responsible for the universe's accelerated expansion.Combined, dark matter and dark energy constitute 95% o
Stars form from collapsing gas clouds and ignite through nuclear fusion.Small stars have long, stable lives, while massive stars burn bright and die young.A star’s death contributes essential elements to the universe, recycling materials for fu
You'll learn:What is a black hole?A region in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape. Black holes form from the collapse of massive stars, creating a point of infinite density known as the singularity.The Even
The early universe was a dense, hot mixture of particles that eventually formed stars and galaxies.Dark energy is causing the universe's expansion to accelerate.
Key concepts discussed include:Wave-particle duality, where light behaves both as a wave and as a particle depending on how it is observed.Superposition, illustrated by Schrödinger’s cat, where particles exist in multiple states simultaneously
"Welcome to Short Science Explained Trailer. Where we break down complex scientific concepts into short, digestible stories.
Unlock more with Podchaser Pro
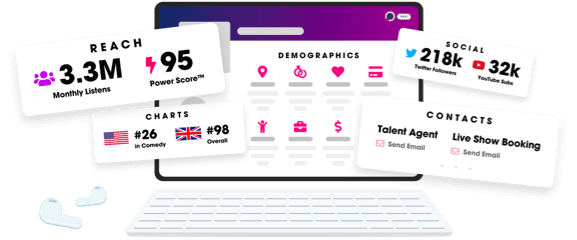
- Audience Insights
- Contact Information
- Demographics
- Charts
- Sponsor History
- and More!
- Account
- Register
- Log In
- Find Friends
- Resources
- Help Center
- Blog
- API
Podchaser is the ultimate destination for podcast data, search, and discovery. Learn More
- © 2025 Podchaser, Inc.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Contact Us
