The Scientist’s LabTalk
Episodes of The Scientist’s LabTalk
Mark All
Synthetic technologies allow scientists to venture into uncharted waters, asking unique research questions and finding previously unattainable solutions to some of life’s biggest mysteries. From gene editing to protein engineering, synthesized
Synthetic technologies allow scientists to venture into uncharted waters, asking unique research questions and finding previously unattainable solutions to some of life’s biggest mysteries. From gene editing to protein engineering, synthesized
Synthetic technologies allow scientists to venture into uncharted waters, asking unique research questions and finding previously unattainable solutions to some of life’s biggest mysteries. From gene editing to protein engineering, synthesized
With a track record of invention and translating technology into practical solutions, Walker Inman continues to drive innovation in the life sciences field. Inman is currently the cofounder and CEO of Lucid Scientific Inc., a company that devel
Lauren Drouin is the director of analytical development and the Genomic Medicine Unit at Alexion AstraZeneca Rare Disease. As a dynamic scientist with unique expertise in current research and industry trends for gene therapies, Drouin is passio
Researchers commonly employ lentiviruses to modify cells genetically. However, they must overcome several challenges when using these viruses in the laboratory or clinic. In this episode, Charlene Lancaster from The Scientist’s Creative Service
Scientists continuously develop new assays to fill unmet diagnostic needs. While methods such as quantitative PCR have emerged as essential tools in molecular diagnostics, scientists developing and administering these assays still must overcome
Scientists continuously develop new assays to fill unmet diagnostic needs. While methods such as quantitative PCR have emerged as essential tools in molecular diagnostics, scientists developing and administering these assays still must overcome
Scientists commonly use qPCR applications in molecular diagnostics to detect pathogens, assess viral loads, or uncover mutations. While the qPCR assay itself may seem straightforward, other aspects such as data collection and security, and foll
Scientists commonly use qPCR applications in molecular diagnostics to detect pathogens, assess viral loads, or uncover mutations. While the qPCR assay itself may seem straightforward, other aspects such as data collection and security, and foll
Welcome to Molecular Diagnostics: An Eye Toward the Future, a special edition podcast series produced by The Scientist’s Creative Services Team. This series is brought to you by Thermo Fisher Scientific, a world leader in serving science. Their
Translational research cannot be conducted in a vacuum. For a translational researcher to be successful, they need to build strong relationships with individuals, companies, and institutions that will provide useful support and expertise. In th
In this episode, Guangping Gao, professor and director of the Horae Gene Therapy Center at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, speaks about developing human gene therapies using recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors, scaling up
Welcome to Building Bridges for Translational Research, a special edition podcast series produced by The Scientist’s Creative Services Team. This series is brought to you by Cytiva, a global provider of technologies and services that advance an
Immunotherapies are promising as a holy grail for cancer treatment, but patient responses to these interventions are often variable in both solid tumors and blood cancers.In this episode, Iris Kulbatski from The Scientist’s Creative Services T
By understanding disease risk through the information found in a person’s genome, scientists can develop more effective therapeutics and clinicians can treat their patients more effectively.In this episode, we talk to Kári Stefánsson, founder
Heterogeneous disorders such as cardiovascular disease have multiple risk factors, causes, and manifestations. Having a holistic view of a patient’s unique biology potentially leads to earlier and better treatment options.In this episode, we t
Biobanks that house data from electronic health records or collect samples directly from participants are precious resources for researchers looking to understand health and disease and translate these discoveries into recommendations and treat
Welcome to The Human Data Era, a special edition podcast series produced by The Scientist’s Creative Services Team.This series is brought to you by Amgen, a pioneer in the science of using living cells to make biologic medicines. They helped i
Through epigenetic mechanisms, some environmental toxicants, such as heavy metals, reversibly alter gene expression patterns that then drive cancer progression. In this episode, Yvonne Fondufe-Mittendorf discusses her work studying environmenta
Substances that enter the body, such as food or chemicals, can make epigenetic changes in the germline that become inherited, affecting the health of future generations. In this episode, Heidi Lempradl discusses her work studying the effects of
Welcome to Exposed: Environmental Echoes in Health, a special edition podcast series produced by The Scientist’s Creative Services Team. This series is brought to you by Van Andel Institute, an independent biomedical research institute devoted
The brain’s intractable nature makes neurodegenerative disorders challenging to study, but modern assays and technologies give scientists a fresh look at this complex organ. In this episode, Niki Spahich from The Scientist’s Creative Services T
Cancer is one therapeutic area where patients cannot wait the conventional 10 or 12 years for a new therapy. For these patients, time is of the essence, and improved access to faster clinical trials can be the difference between receiving a new
With advances in genetics and other human data, researchers and doctors will one day be able to practice precision medicine. However, predicting how a patient will respond to a medicine is challenging in under-represented patients who are often
Unlock more with Podchaser Pro
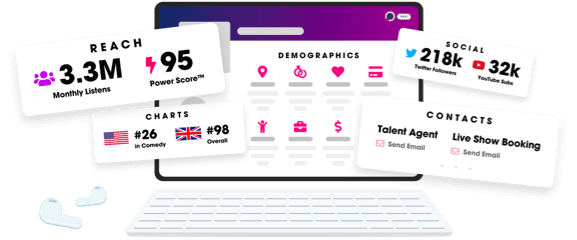
- Audience Insights
- Contact Information
- Demographics
- Charts
- Sponsor History
- and More!
- Account
- Register
- Log In
- Find Friends
- Resources
- Help Center
- Blog
- API
Podchaser is the ultimate destination for podcast data, search, and discovery. Learn More
- © 2025 Podchaser, Inc.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Contact Us
